
Understanding ADHD and Autism
Understanding ADHD and Autism: Prevalence, Overlap, and Management Strategies
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) and Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) are neurodevelopmental conditions that significantly impact individuals’ lives. Understanding their prevalence, distinguishing features, overlapping characteristics, and effective management strategies is crucial for fostering supportive environments.
Prevalence in the UK
- ADHD: Approximately 5% of children globally are diagnosed with ADHD, with UK-specific data aligning closely with this figure.
- Autism: Recent studies indicate that about 1.57% of children in the UK are diagnosed with autism.
Distinct Characteristics
- ADHD: Characterized by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, leading to challenges in maintaining focus, organizing tasks, and controlling impulses.
- Autism: Marked by difficulties in social communication and interaction, alongside restricted and repetitive behaviors. Individuals may exhibit intense focus on specific interests and a preference for routine.
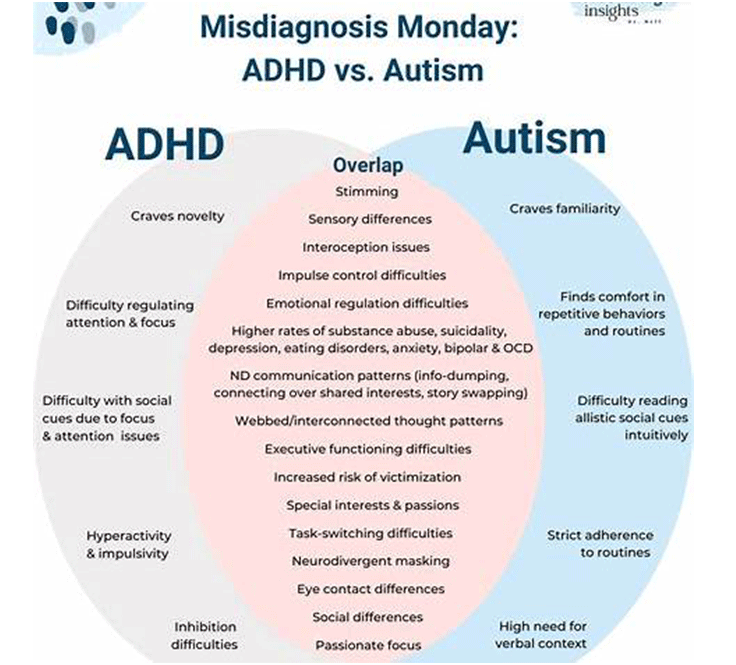
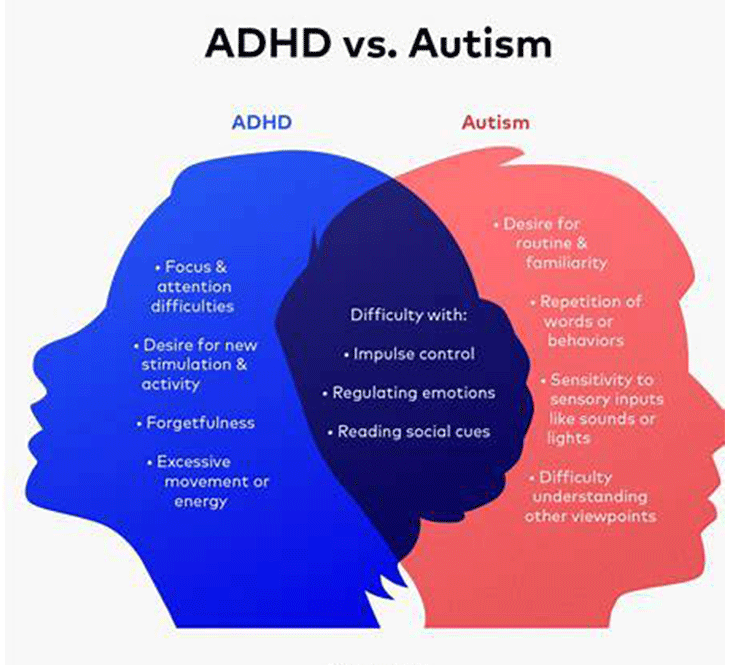
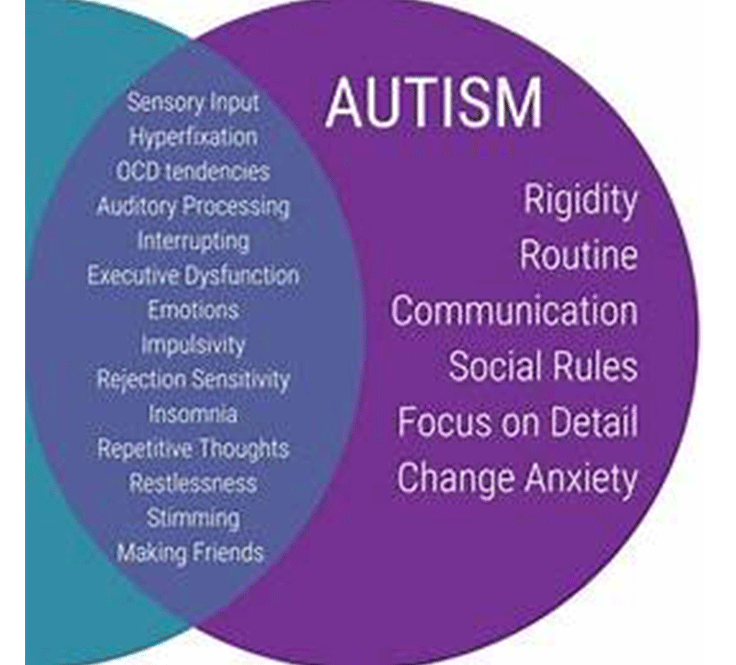
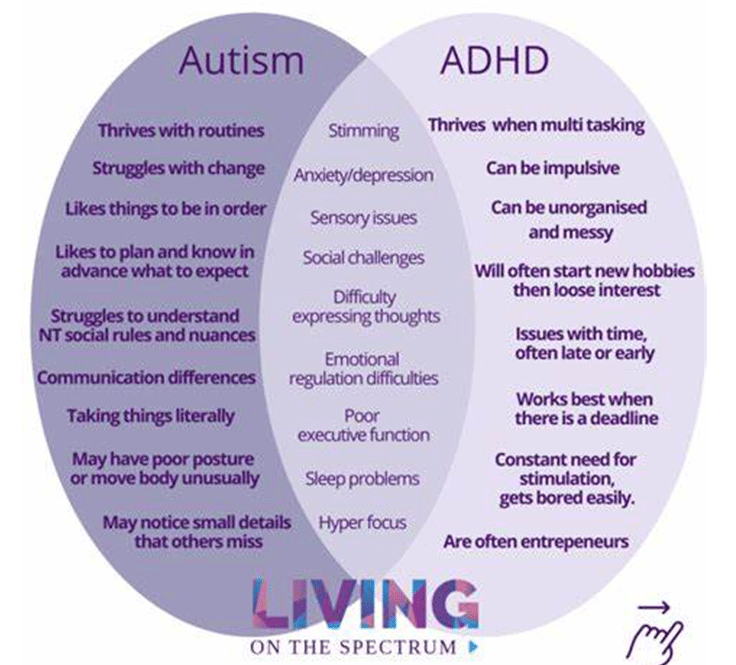
Overlap Between ADHD and Autism
ADHD and autism often co-occur, a condition sometimes referred to as AuDHD. Research suggests that many individuals with one diagnosis exhibit traits of the other. Common overlapping experiences include sensory differences, intense focus on specific interests, executive dysfunction, sleep issues, and emotional dysregulation. Autistica
Management Strategies
Effective management of ADHD and autism involves a combination of approaches tailored to individual needs:
- Behavioral Interventions: Techniques such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) for autism and Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for ADHD can help modify behaviors and develop coping strategies.
- Educational Support: Implementing individualized education plans (IEPs) and providing accommodations like extended time for tests or a quiet workspace can enhance learning experiences.
- Medication: For ADHD, stimulant medications like methylphenidate are commonly prescribed. In cases of co-occurring autism, careful monitoring is essential due to potential atypical responses.
- Therapies: Speech and language therapy, occupational therapy, and social skills training can address specific challenges associated with both conditions.
- Family and Community Support: Educating families and communities fosters understanding and creates supportive environments for individuals with ADHD and autism.
Enhancing Management Approaches
To improve outcomes for individuals with ADHD and autism, consider the following:
- Early Diagnosis: Prompt identification allows for timely intervention, which can significantly improve quality of life.
- Integrated Care: Coordinating services among healthcare providers, educators, and families ensures comprehensive support.
- Personalized Strategies: Tailoring interventions to individual strengths and challenges promotes more effective management.
- Public Awareness: Increasing societal understanding reduces stigma and encourages inclusive practices.
By adopting these strategies, we can better support individuals with ADHD and autism, enabling them to lead fulfilling lives.



Leave a Reply